
The essential feature of the MAC addresses is the delivery of a frame on layer 2. The function of MAC addresses in the network Less common is the bit-reversed or non-canonical form. A distinction can be in between the canonical and the bit-reversed description. The most common is the authoritative description. It consists, as already described, of a sequence of two-digit hexadecimal numbers, separated by a hyphen (sometimes also by a colon).
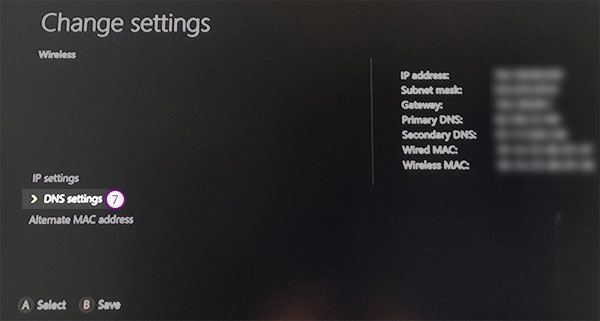
There are various forms of representation of MAC addresses. The different forms of representation of MAC addresses The manufacturer specified the last three bytes of address. It assigns this bit sequence only once, thus ensuring that the complete address is unique. The spelling is usually in hexadecimal form, where hyphens or colons separate the bytes. Subsequently, until the end of the third byte, the manufacturer identifier of the network card or hardware follows. The bit sequence is called Organizationally Unique Identifier (OUI) and is awarded by the IEEE to the various manufacturers of the appliance. The structure of the 48-bit address is precisely defined. The first two bits specify the type of speech. Among other things, they determine whether it is a multicast or broadcast address or a globally unique individual address. On Windows devices, the MAC address is also displayed as a “physical address,” on Apple devices as “Airport ID.”.The 12-digit code is displayed in the hexadecimal system and is unique to your device. The first six digits indicate from which manufacturer your network adapter is. The second six numbers represent the specific number for your device.The MAC address assigns to your network adapter. You need this to be able to use the Internet via LAN or WLAN.“MAC” stands for “ Media Access Control,” this address is used to identify your device.You do not need to be a computer expert to know what a MAC address is. It is a unique address for devices with network capabilities. We explain what you should know about the MAC address. Unique MAC addresses and their function.
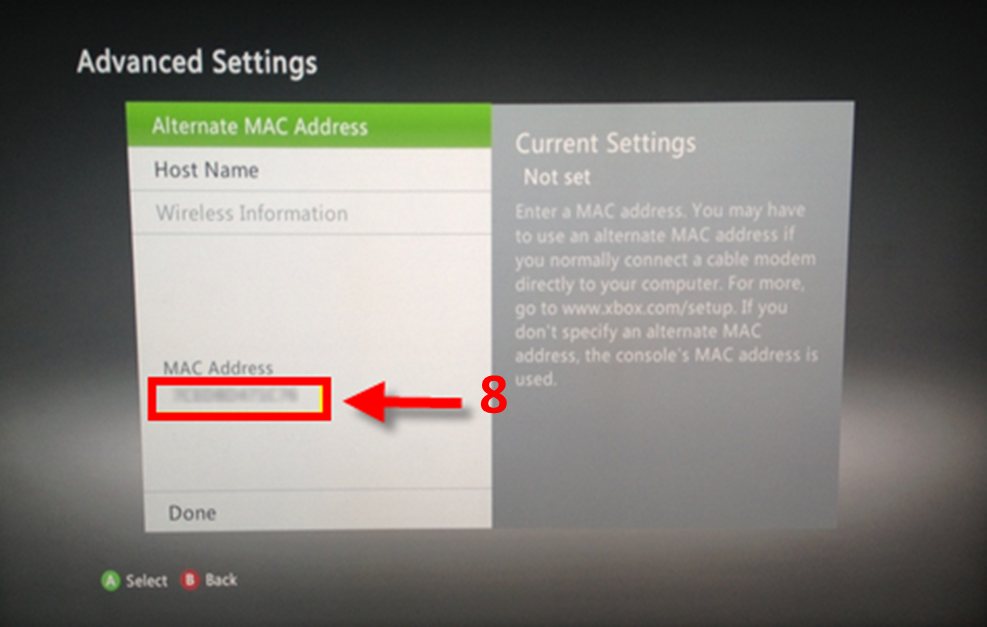
The function of MAC addresses in the network.
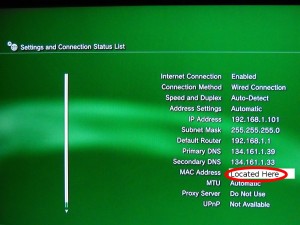


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
